Firebase Storage: Used for storing files (mostly user-generated) which can be images, videos, audio, and more. They are usually not changed often.
Cloud Firestore: Used for storing structured data which can be used to create a NoSQL database.
Firebase offers a variety of storage options for Flutter apps. The most commonly used are Firebase Storage and Cloud Firestore.
Firebase Storage: Used for storing files (mostly user-generated) which can be images, videos, audio, and more. They are usually not changed often.
Cloud Firestore: Used for storing structured data which can be used to create a NoSQL database.
You need to follow steps here to get started. You should create Cloud Firestore in Firebase Console first.
We use Cloud Firestore to store product’s information. It is parsed in product model in the code.
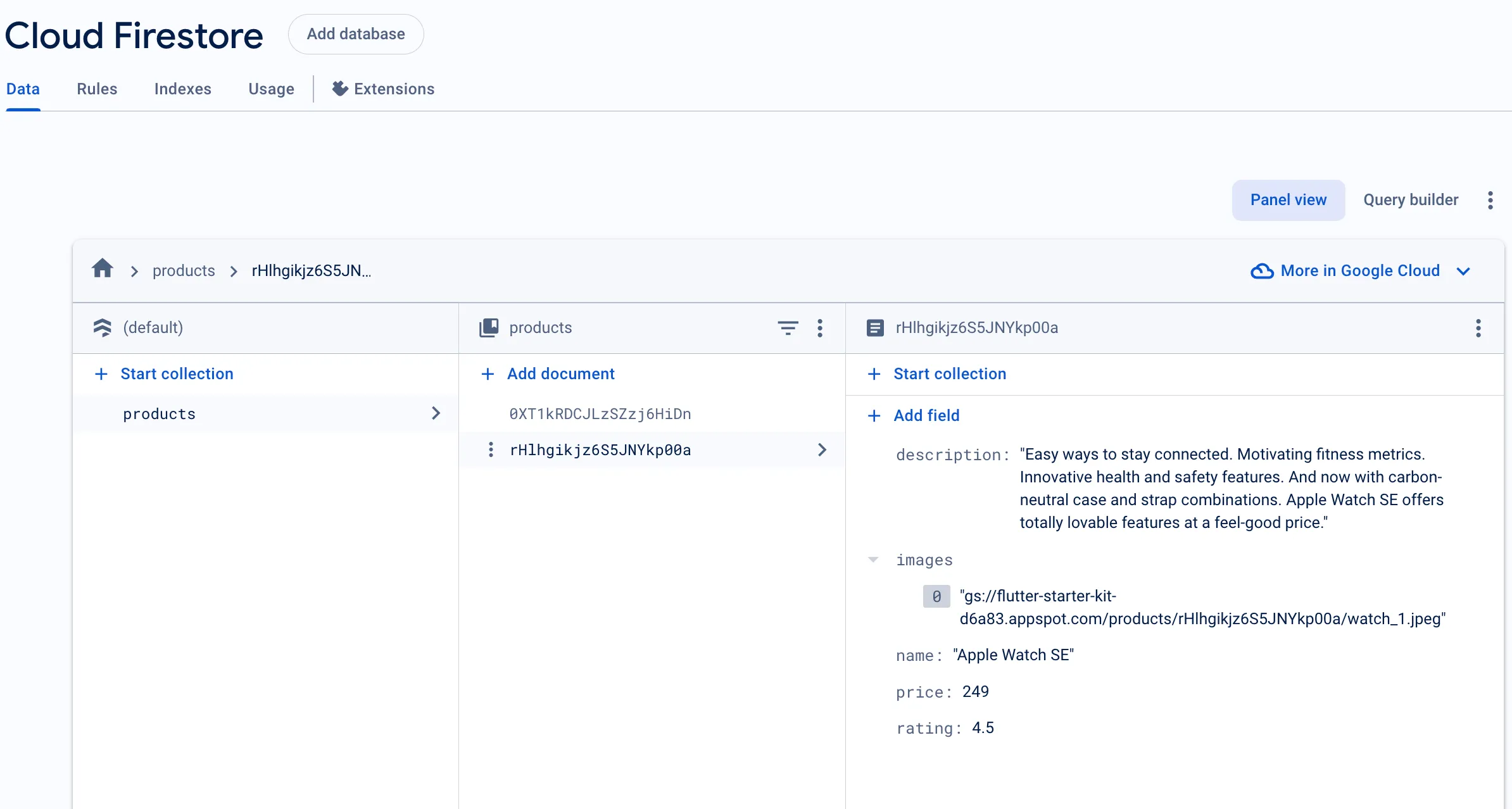
Pay attention to Cloud Firestore rules. Here is the one to allow read operation for everyone:
rules_version = '2';service cloud.firestore { match /databases/{database}/documents { match /{document=**} { allow read: if true; } }}Read more about security here
It is a storage service used to store and retrieve user generated content. They are generally used to store big blobs of data that don’t change often like photos, audio, videos, docs, etc.
Go to Firebase console -> Build -> Storage -> Get Started. Choose Test mode for starters and cloud storage location (preferably near your location).
Note: storage location cannot be changed after creation.
Once the bucket is created, data can be organized into directories based on schema of your choice. For the purpose of this project, we will be using Firebase Storage to store user uploaded profile images and product images.
Upload locations
📸 Profile pictues: Used for storing user uploaded profile images. user_uploads/profile/$userId/$imageName.$fileExtension
📸 Product images: Used for storing product images. It is stored in products/$productId/$imageName.$fileExtension
Note: Firebase Storage creates folders and subfolders based on the path provided, if the path does not already exist.
For now, we will be allowing all users to read and write to the storage. This is not recommended for production:
rules_version = '2';service firebase.storage { match /b/{bucket}/o { // This rule allows anyone with your Storage bucket reference to view, edit, // and delete all data in your Storage bucket. match /{allPaths=**} { allow read, write: if true; } }}More granular security rule would be:
rules_version = '2';service firebase.storage { match /b/{bucket}/o { // Allow read access to all files match /{allPaths=**} { allow read: if true; }
// Allow authenticated users to write to their own profile pictures match /user_uploads/profile/{userId}/{fileName} { allow write: if request.auth != null && request.auth.uid == userId; } }}Read more about security rules here